🧪 What Is Cooking Oil Made Of? A Deep Dive into Its Chemistry and Culinary Power
What Is Cooking Oil Made Of? Understanding Its Chemistry, Nutrition & Culinary Power
Cooking oil is more than a kitchen essential — it is a scientifically complex blend of fatty acids and bioactive compounds that influence nutrition, cooking performance, shelf stability, and global trade value.
At Cavin Enterprise, we supply export-ready edible oils supported by full documentation, fatty acid profiles, and batch traceability. Understanding cooking oil composition helps buyers choose the right oil for retail, foodservice, or industrial applications.
In this guide, we explore the chemical structure of cooking oil, its nutritional impact, and why smoke point matters for culinary performance.
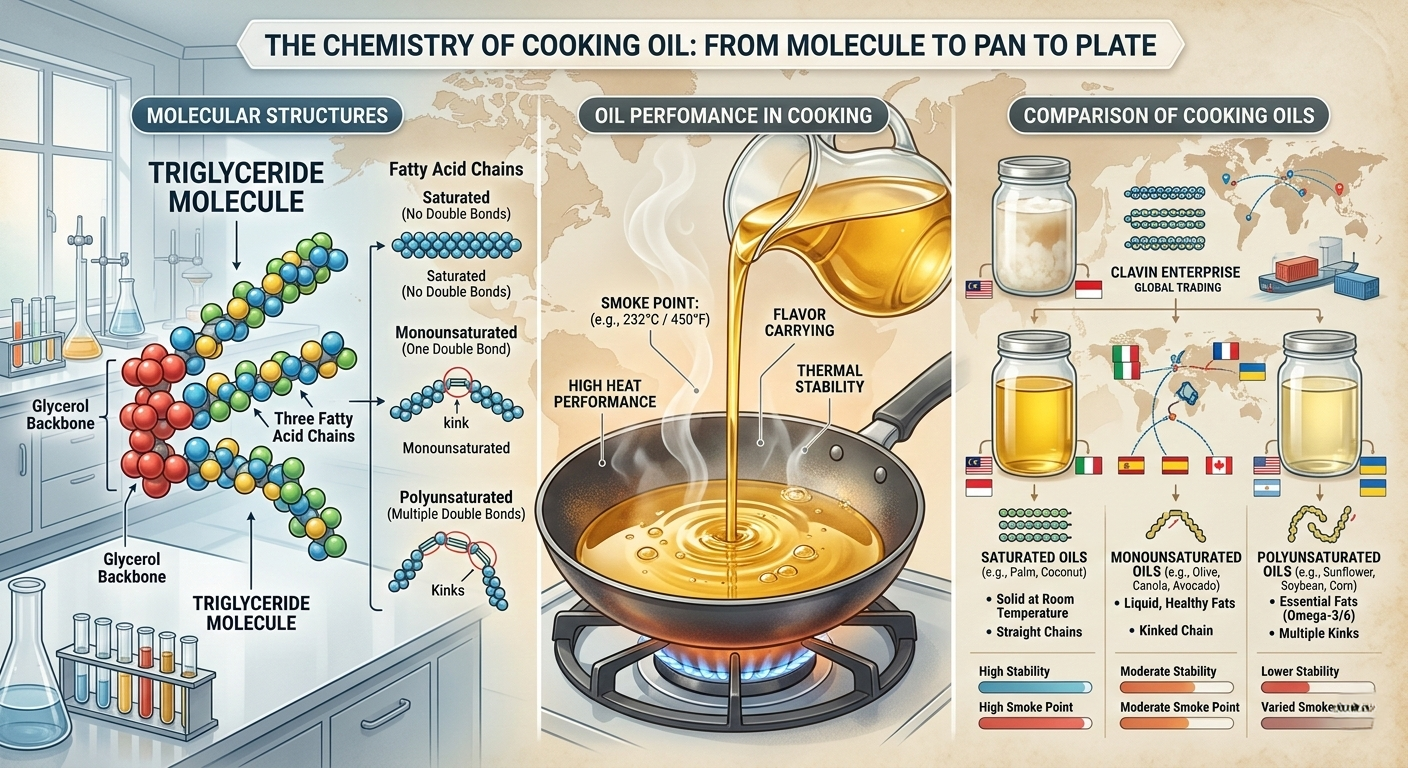
🧬 The Chemical Composition of Cooking Oil
Cooking oils are primarily composed of triglycerides, which are molecules made of glycerol bonded to three fatty acids. The type and ratio of fatty acids determine:
-
Nutritional value
-
Oxidative stability
-
Flavor profile
-
Smoke point
-
Shelf life
🔹 1. Saturated Fats
Examples: Coconut oil, palm oil
-
Typically solid at room temperature
-
Highly stable under high heat
-
Resistant to oxidation
-
Commonly used in baking and deep frying
Saturated fats provide strong thermal stability, making them suitable for industrial and commercial frying applications.
🔹 2. Monounsaturated Fats (MUFA)
Examples: Olive oil, avocado oil
-
Liquid at room temperature
-
Known for heart-health benefits
-
Moderate to high smoke points
-
Ideal for sautéing and salad dressings
Monounsaturated fats are often preferred in premium retail markets due to their perceived health benefits.
🔹 3. Polyunsaturated Fats (PUFA)
Examples: Flaxseed oil, walnut oil, hemp oil
-
Contain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
-
Highly sensitive to heat and light
-
Best used in cold applications
-
Require protective packaging
These oils are popular in wellness markets but require careful storage to prevent oxidation.
🔥 Smoke Point: Why It Matters in Cooking & Trade
The smoke point of cooking oil is the temperature at which it begins to break down and release visible smoke. When oil exceeds this temperature:
-
Nutrients degrade
-
Flavor changes
-
Harmful compounds may form
-
Oil oxidizes faster
Approximate Smoke Points:
-
Refined palm olein: High (ideal for frying)
-
Olive oil (extra virgin): Moderate
-
Sunflower oil (refined): High
-
Flaxseed oil: Low (not suitable for frying)
For foodservice and industrial buyers, high smoke point oils reduce waste and improve cost efficiency.
🌍 Why Cooking Oil Chemistry Matters for Global Buyers
Understanding fatty acid composition and oxidative stability helps buyers:
-
Choose oils for high-heat cooking
-
Select heart-healthy retail products
-
Meet labeling regulations
-
Ensure longer shelf life in export markets
-
Match oil type to culinary application
Fatty acid profiles are particularly important in bulk and private label edible oil trade.
🧾 Cavin Enterprise Quality & Compliance Standards
Every batch of oil exported by Cavin Enterprise includes:
✅ Certificate of Analysis (COA) with full fatty acid profile
✅ MSDS documentation
✅ Batch traceability system
✅ Certificate of origin & HS code
✅ Multilingual label translations (Arabic, French, Spanish)
✅ Private label packaging options
We ensure that every shipment meets international safety, documentation, and nutritional transparency standards.








